# 构建与初始化
# 构建版本
通常我们利用 vue-cli 去初始化我们的 Vue.js 项目的时候会询问我们用 Runtime Only 版本的还是 Runtime + Compiler 版本。
# Runtime only
编译时转化,离线编译。
Runtime Only 版本通常需要借助如 webpack 的 vue-loader ⼯具把 .vue ⽂件编译成 JavaScript,因为是在编译阶段做的,所以它只包含运⾏时的 Vue.js 代码,因此代码体积也会 更轻量,性能更优。
# Runtime + Compiler
运行时,客户端编译。
如果没有对代码做预编译,但又使用了 Vue 的 template 属性并传入一个字符串,则需要在客户端编译模板,即运行时编译。因为在 Vue2.0 中,最终渲染都是通过 render 函数,如果写 template 属性,则需要编译成 render 函数,那么这个编译过程会发生运行时,所以需要带有编译器的版本。很显然,这个编译过程对性能会有一定损耗,所以通常我们更推荐使用 Runtime-Only 的 Vue.js。
# 初始化
当代码执行 import Vue from 'vue' 的时候,是从这个入口执行代码来初始化 Vue。Vue 实际是一个用 Function 实现的类,只能通过 new Vue() 实例化。
为何 Vue 不用 ES6 的 Class 去实现呢?
在 Vue 初始化文件中有很多 xxxMixin 的函数调用,并把 Vue 当参数传入,它们的功能都是给 Vue 的 prototype 上扩展一些方法,Vue 按功能把这些扩展分散到多个模块中去实现,而不是在一个模块里实现所有,这种方式是用 Class 难以实现的。这么做的好处是非常方便代码的维护和管理,这种编程技巧也非常值得我们去学习。
Vue.js 在整个初始化过程中,除了给它的原型 prototype 上扩展方法,还会通过 initGlobalAPI 给 Vue 这个对象本身扩展全局的静态方法,即 Vue 的 全局API (opens new window)。
import { initMixin } from './init'
import { stateMixin } from './state'
import { renderMixin } from './render'
import { eventsMixin } from './events'
import { lifecycleMixin } from './lifecycle'
import { warn } from '../util/index'
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
renderMixin(Vue)
export default Vue
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Vue 初始化主要就干了以下几件事情:合并配置,初始化生命周期,初始化事件中心,初始化渲染,初始化 data、props、computed、watcher 等等。在初始化的最后,检测到如果有 el 属性,则调用 vm.$mount 方法挂载 vm,挂载的目标就是把模板渲染成最终的 DOM。
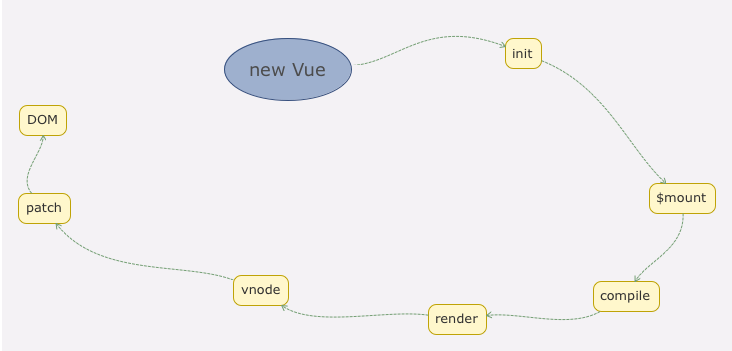
# new Vue 发生了什么 - init
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
const vm: Component = this
// a uid
vm._uid = uid++
let startTag, endTag
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
startTag = `vue-perf-start:${vm._uid}`
endTag = `vue-perf-end:${vm._uid}`
mark(startTag)
}
// a flag to avoid this being observed
vm._isVue = true
// merge options
if (options && options._isComponent) {
// optimize internal component instantiation
// since dynamic options merging is pretty slow, and none of the
// internal component options needs special treatment.
/**
* 每个子组件初始化时走这里,这里只做了一些性能优化
* 将组件配置对象上的一些深层次属性放到 vm.$options 选项中,以提高代码的执行效率
*/
initInternalComponent(vm, options)
} else {
/**
* 初始化根组件时走这里,合并 Vue 的全局配置到根组件的局部配置,比如 Vue.component 注册的全局组件会合并到 根实例的 components 选项中
* 至于每个子组件的选项合并则发生在两个地方:
* 1、Vue.component 方法注册的全局组件在注册时做了选项合并
* 2、{ components: { xx } } 方式注册的局部组件在执行编译器生成的 render 函数时做了选项合并,包括根组件中的 components 配置
*/F
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
)
}
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
// 设置代理,将 vm 实例上的属性代理到 vm._renderProxy
initProxy(vm)
} else {
vm._renderProxy = vm
}
// expose real self
vm._self = vm
// 初始化组件实例关系属性,比如 $parent、$children、$root、$refs 等
initLifecycle(vm)
/**
* 初始化自定义事件,这里需要注意一点,所以我们在 <comp @click="handleClick" /> 上注册的事件,监听者不是父组件, 而是子组件本身,也就是说事件的派发和监听者都是子组件本身,和父组件无关
*/
initEvents(vm)
// 解析组件的插槽信息,得到 vm.$slot,处理渲染函数,得到 vm.$createElement 方法,即 h 函数,将render函数转为vnode的方法
initRender(vm)
// 调用 beforeCreate 钩子函数
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
// 初始化组件的 inject 配置项,得到 result[key] = val 形式的配置对象,然后对结果数据进行响应式处理,并代理每个 key 到 vm 实例
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
// 数据响应式的重点,处理 props、methods、data、computed、watch
initState(vm)
// 解析组件配置项上的 provide 对象,将其挂载到 vm._provided 属性上
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
// 调用 created 钩子函数
callHook(vm, 'created')
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${vm._name} init`, startTag, endTag)
}
// 如果发现配置项上有 el 选项,则自动调用 $mount 方法,也就是说有了 el 选项,就不需要再手动调用 $mount,反之,没有 el 则必须手动调用 $mount
if (vm.$options.el) {
// 调用 $mount 方法,进入挂载阶段
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
Vue 初始化主要就干了几件事情,合并配置,初始化生命周期,初始化事件中心,初始化渲染,执行 beforeCreate 钩子,初始化依赖注入内容、初始化 prop、methods、data、computed、watcher ,解析组件配置项上的 provide 对象,执行 created 钩子, 最后 mount 挂载真实 DOM 。
# Vue 实例挂载 - $mount
Vue 中是通过 $mount 实例方法去挂载 vm 的,$mount 方法的实现是和平台、构建方式相关。
// src\platforms\web\entry-runtime-with-compiler.js
const idToTemplate = cached(id => {
const el = query(id)
return el && el.innerHTML
})
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && query(el)
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.`
)
return this
}
const options = this.$options
// resolve template/el and convert to render function
if (!options.render) {
let template = options.template
if (template) {
if (typeof template === 'string') {
if (template.charAt(0) === '#') {
template = idToTemplate(template)
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !template) {
warn(
`Template element not found or is empty: ${options.template}`,
this
)
}
}
} else if (template.nodeType) {
template = template.innerHTML
} else {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn('invalid template option:' + template, this)
}
return this
}
} else if (el) {
template = getOuterHTML(el)
}
if (template) {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
mark('compile')
}
const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, {
outputSourceRange: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production',
shouldDecodeNewlines,
shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref,
delimiters: options.delimiters,
comments: options.comments
}, this)
options.render = render
options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
mark('compile end')
measure(`vue ${this._name} compile`, 'compile', 'compile end')
}
}
}
// 原先原型上的 $mount 方法
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
首先,对 el 做了限制,Vue 不能挂载在 body、html 这样的根节点上。接下来的是很关键的逻辑 —— 如果没有定义 render 方法,则会把 el 或者 template 字符串转换成 render 方法。在 Vue 2.0 版本中,所有 Vue 的组件的渲染最终都需要 render 方法,无论我们是用单文件 .vue 方式开发组件,还是写了 el 或者 template 属性,最终都会转换成 render 方法,那么这个过程是 Vue 的一个“在线编译”的过程,它是调用 compileToFunctions 方法实现的,编译过程我们之后会介绍。最后,调用原先原型上的 $mount 方法挂载。
原先原型上的 $mount 方法如下:
// public mount method
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined
return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
$mount 方法支持传入 2 个参数,第一个是 el,它表示挂载的元素,可以是字符串,也可以是 DOM 对象,如果是字符串在浏览器环境下会调用 query 方法转换成 DOM 对象的。第二个参数是和服务端渲染相关,在浏览器环境下我们不需要传第二个参数。$mount 方法实际上会去调用 mountComponent 方法
// src\core\instance\lifecycle.js
export function mountComponent (
vm: Component,
el: ?Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
vm.$el = el
if (!vm.$options.render) {
vm.$options.render = createEmptyVNode
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if ((vm.$options.template && vm.$options.template.charAt(0) !== '#') ||
vm.$options.el || el) {
warn(
'You are using the runtime-only build of Vue where the template ' +
'compiler is not available. Either pre-compile the templates into ' +
'render functions, or use the compiler-included build.',
vm
)
} else {
warn(
'Failed to mount component: template or render function not defined.',
vm
)
}
}
}
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount')
let updateComponent
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
updateComponent = () => {
const name = vm._name
const id = vm._uid
const startTag = `vue-perf-start:${id}`
const endTag = `vue-perf-end:${id}`
mark(startTag)
const vnode = vm._render()
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} render`, startTag, endTag)
mark(startTag)
vm._update(vnode, hydrating)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} patch`, startTag, endTag)
}
} else {
updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
}
// we set this to vm._watcher inside the watcher's constructor
// since the watcher's initial patch may call $forceUpdate (e.g. inside child
// component's mounted hook), which relies on vm._watcher being already defined
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before () {
if (vm._isMounted && !vm._isDestroyed) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */)
hydrating = false
// manually mounted instance, call mounted on self
// mounted is called for render-created child components in its inserted hook
if (vm.$vnode == null) {
vm._isMounted = true
callHook(vm, 'mounted')
}
return vm
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
mountComponent 核心就是先实例化一个渲染Watcher,在它的回调函数中会调用 updateComponent 方法,在此方法中调用 vm._render 方法先生成虚拟 Node,最终调用 vm._update 更新 DOM。Watcher 在这里起到两个作用,一个是初始化的时候会执行回调函数,另一个是当 vm 实例中的监测的数据发生变化的时候执行回调函数。函数最后判断为根节点的时候设置 vm._isMounted 为 true, 表示这个实例已经挂载了,同时执行 mounted 钩子函数。 这里注意 vm.$vnode 表示 Vue 实例的父虚拟 Node,所以它为 Null 则表示当前是根 Vue 的实例。mountComponent 会完成整个渲染工作,包含最核心的 2 个方法:vm._render 和 vm._update。
compiler 编译过程由 compileToFunctions 完成,具体编译过程见 模板编译与渲染
# 渲染 DOM - render
Vue 的 _render 方法是实例的一个私有方法,它用来把实例渲染成一个虚拟 Node。
// src\core\instance\render.js
Vue.prototype._render = function (): VNode {
const vm: Component = this
const { render, _parentVnode } = vm.$options
if (_parentVnode) {
vm.$scopedSlots = normalizeScopedSlots(
_parentVnode.data.scopedSlots,
vm.$slots
)
}
// set parent vnode. this allows render functions to have access
// to the data on the placeholder node.
vm.$vnode = _parentVnode
// render self
let vnode
try {
vnode = render.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, vm, `render`)
// return error render result,
// or previous vnode to prevent render error causing blank component
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && vm.$options.renderError) {
try {
vnode = vm.$options.renderError.call(vm._renderProxy, vm.$createElement, e)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, vm, `renderError`)
vnode = vm._vnode
}
} else {
vnode = vm._vnode
}
}
// if the returned array contains only a single node, allow it
if (Array.isArray(vnode) && vnode.length === 1) {
vnode = vnode[0]
}
// return empty vnode in case the render function errored out
if (!(vnode instanceof VNode)) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && Array.isArray(vnode)) {
warn(
'Multiple root nodes returned from render function. Render function ' +
'should return a single root node.',
vm
)
}
vnode = createEmptyVNode()
}
// set parent
vnode.parent = _parentVnode
return vnode
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
vm._render 最终是通过执行 createElement 方法并返回的是 vnode,它是一个虚拟 Node
# 生成虚拟 DOM - createElement
Vue 利用 createElement 方法创建 VNode。createElement 方法实际上是对 _createElement 方法的封装。
// src\core\vdom\create-element.js
export function createElement (
context: Component,
tag: any,
data: any,
children: any,
normalizationType: any,
alwaysNormalize: boolean
): VNode | Array<VNode> {
if (Array.isArray(data) || isPrimitive(data)) {
normalizationType = children
children = data
data = undefined
}
if (isTrue(alwaysNormalize)) {
normalizationType = ALWAYS_NORMALIZE
}
return _createElement(context, tag, data, children, normalizationType)
}
export function _createElement (
context: Component,
tag?: string | Class<Component> | Function | Object,
data?: VNodeData,
children?: any,
normalizationType?: number
): VNode | Array<VNode> {
if (isDef(data) && isDef((data: any).__ob__)) {
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn(
`Avoid using observed data object as vnode data: ${JSON.stringify(data)}\n` +
'Always create fresh vnode data objects in each render!',
context
)
return createEmptyVNode()
}
// object syntax in v-bind
if (isDef(data) && isDef(data.is)) {
tag = data.is
}
if (!tag) {
// in case of component :is set to falsy value
return createEmptyVNode()
}
// warn against non-primitive key
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
isDef(data) && isDef(data.key) && !isPrimitive(data.key)
) {
if (!__WEEX__ || !('@binding' in data.key)) {
warn(
'Avoid using non-primitive value as key, ' +
'use string/number value instead.',
context
)
}
}
// support single function children as default scoped slot
if (Array.isArray(children) &&
typeof children[0] === 'function'
) {
data = data || {}
data.scopedSlots = { default: children[0] }
children.length = 0
}
if (normalizationType === ALWAYS_NORMALIZE) {
children = normalizeChildren(children)
} else if (normalizationType === SIMPLE_NORMALIZE) {
children = simpleNormalizeChildren(children)
}
let vnode, ns
if (typeof tag === 'string') {
let Ctor
ns = (context.$vnode && context.$vnode.ns) || config.getTagNamespace(tag)
if (config.isReservedTag(tag)) {
// platform built-in elements
vnode = new VNode(
config.parsePlatformTagName(tag), data, children,
undefined, undefined, context
)
} else if ((!data || !data.pre) && isDef(Ctor = resolveAsset(context.$options, 'components', tag))) {
// component
vnode = createComponent(Ctor, data, context, children, tag)
} else {
// unknown or unlisted namespaced elements
// check at runtime because it may get assigned a namespace when its
// parent normalizes children
vnode = new VNode(
tag, data, children,
undefined, undefined, context
)
}
} else {
// direct component options / constructor
vnode = createComponent(tag, data, context, children)
}
if (Array.isArray(vnode)) {
return vnode
} else if (isDef(vnode)) {
if (isDef(ns)) applyNS(vnode, ns)
if (isDef(data)) registerDeepBindings(data)
return vnode
} else {
return createEmptyVNode()
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
_createElement 方法有 5 个参数:
- context 表示 VNode 的上下文环境,它是 Component 类型
- tag 表示标签,它可以是一个字符串,也可以是一个 Component
- data 表示 VNode 的数据,它是一个 VNodeData 类型
- children 表示当前 VNode 的子节点,它是任意类型的,它接下来需要被规范为标准的 VNode 数组
- normalizationType 表示子节点规范的类型,类型不同规范的方法也就不一样,它主要是参考 render 函数是编译生成的还是用户手写的。经过对 children 的规范化,children 变成了一个类型为 VNode 的 Array
每个 VNode 有 children,children 的每个元素也是一个 VNode,这样就形成了一个 VNode Tree,它很好的描述了我们的 DOM Tree。
回到 mountComponent 函数的过程,我们已经知道 vm._render 是如何创建了一个 VNode,接下来就是要把这个 VNode 渲染成一个真实的 DOM 并渲染出来,这个过程是通过 vm._update 完成
# 渲染真实 Dom - update
Vue 的 _update 是实例的一个私有方法,它被调用的时机有 2 个,一个是首次渲染,一个是数据更新的时候。_update 方法的作用是把 VNode 渲染成真实的 DOM。
// src\core\instance\lifecycle.js
Vue.prototype._update = function (vnode: VNode, hydrating?: boolean) {
const vm: Component = this
const prevEl = vm.$el
const prevVnode = vm._vnode
const restoreActiveInstance = setActiveInstance(vm)
vm._vnode = vnode
// Vue.prototype.__patch__ is injected in entry points
// based on the rendering backend used.
if (!prevVnode) {
// initial render
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(vm.$el, vnode, hydrating, false /* removeOnly */)
} else {
// updates
vm.$el = vm.__patch__(prevVnode, vnode)
}
restoreActiveInstance()
// update __vue__ reference
if (prevEl) {
prevEl.__vue__ = null
}
if (vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = vm
}
// if parent is an HOC, update its $el as well
if (vm.$vnode && vm.$parent && vm.$vnode === vm.$parent._vnode) {
vm.$parent.$el = vm.$el
}
// updated hook is called by the scheduler to ensure that children are
// updated in a parent's updated hook.
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
_update 的核心就是调用 vm.patch 方法,这个方法实际上在不同的平台有不同的实现方式。比如,服务端渲染中,没有真实的浏览器 DOM 环境,所以不需要把 VNode 最终转换成 DOM,因此是一个空函数,而在浏览器端渲染中,它指向了 patch 方法。
// src/platforms/web/runtime/patch.js
import * as nodeOps from 'web/runtime/node-ops'
import { createPatchFunction } from 'core/vdom/patch'
import baseModules from 'core/vdom/modules/index'
import platformModules from 'web/runtime/modules/index'
// the directive module should be applied last, after all
// built-in modules have been applied.
const modules = platformModules.concat(baseModules)
export const patch: Function = createPatchFunction({ nodeOps, modules })
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
该方法的定义是调用 createPatchFunction 方法的返回值,这里传入了一个对象,包含 nodeOps 参数和 modules 参数。其中,nodeOps 封装了一系列 DOM 操作的方法,modules 定义了一些模块的钩子函数的实现。
// src\core\vdom\patch.js
export const emptyNode = new VNode('', {}, [])
const hooks = ['create', 'activate', 'update', 'remove', 'destroy']
// ...
export function createPatchFunction (backend) {
let i, j
const cbs = {}
const { modules, nodeOps } = backend
for (i = 0; i < hooks.length; ++i) {
cbs[hooks[i]] = []
for (j = 0; j < modules.length; ++j) {
if (isDef(modules[j][hooks[i]])) {
cbs[hooks[i]].push(modules[j][hooks[i]])
}
}
}
function emptyNodeAt (elm) {
return new VNode(nodeOps.tagName(elm).toLowerCase(), {}, [], undefined, elm)
}
function createRmCb (childElm, listeners) {
function remove () {
if (--remove.listeners === 0) {
removeNode(childElm)
}
}
remove.listeners = listeners
return remove
}
function removeNode (el) {
const parent = nodeOps.parentNode(el)
// element may have already been removed due to v-html / v-text
if (isDef(parent)) {
nodeOps.removeChild(parent, el)
}
}
function isUnknownElement (vnode, inVPre) {
return (
!inVPre &&
!vnode.ns &&
!(
config.ignoredElements.length &&
config.ignoredElements.some(ignore => {
return isRegExp(ignore)
? ignore.test(vnode.tag)
: ignore === vnode.tag
})
) &&
config.isUnknownElement(vnode.tag)
)
}
let creatingElmInVPre = 0
function createElm (
vnode,
insertedVnodeQueue,
parentElm,
refElm,
nested,
ownerArray,
index
) {
if (isDef(vnode.elm) && isDef(ownerArray)) {
// This vnode was used in a previous render!
// now it's used as a new node, overwriting its elm would cause
// potential patch errors down the road when it's used as an insertion
// reference node. Instead, we clone the node on-demand before creating
// associated DOM element for it.
vnode = ownerArray[index] = cloneVNode(vnode)
}
vnode.isRootInsert = !nested // for transition enter check
if (createComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm)) {
return
}
const data = vnode.data
const children = vnode.children
const tag = vnode.tag
if (isDef(tag)) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (data && data.pre) {
creatingElmInVPre++
}
if (isUnknownElement(vnode, creatingElmInVPre)) {
warn(
'Unknown custom element: <' + tag + '> - did you ' +
'register the component correctly? For recursive components, ' +
'make sure to provide the "name" option.',
vnode.context
)
}
}
vnode.elm = vnode.ns
? nodeOps.createElementNS(vnode.ns, tag)
: nodeOps.createElement(tag, vnode)
setScope(vnode)
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (__WEEX__) {
// in Weex, the default insertion order is parent-first.
// List items can be optimized to use children-first insertion
// with append="tree".
const appendAsTree = isDef(data) && isTrue(data.appendAsTree)
if (!appendAsTree) {
if (isDef(data)) {
invokeCreateHooks(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
}
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
}
createChildren(vnode, children, insertedVnodeQueue)
if (appendAsTree) {
if (isDef(data)) {
invokeCreateHooks(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
}
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
}
} else {
createChildren(vnode, children, insertedVnodeQueue)
if (isDef(data)) {
invokeCreateHooks(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
}
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && data && data.pre) {
creatingElmInVPre--
}
} else if (isTrue(vnode.isComment)) {
vnode.elm = nodeOps.createComment(vnode.text)
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
} else {
vnode.elm = nodeOps.createTextNode(vnode.text)
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
}
}
function createComponent (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm) {
let i = vnode.data
if (isDef(i)) {
const isReactivated = isDef(vnode.componentInstance) && i.keepAlive
if (isDef(i = i.hook) && isDef(i = i.init)) {
i(vnode, false /* hydrating */)
}
// after calling the init hook, if the vnode is a child component
// it should've created a child instance and mounted it. the child
// component also has set the placeholder vnode's elm.
// in that case we can just return the element and be done.
if (isDef(vnode.componentInstance)) {
initComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
if (isTrue(isReactivated)) {
reactivateComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm)
}
return true
}
}
}
function initComponent (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) {
if (isDef(vnode.data.pendingInsert)) {
insertedVnodeQueue.push.apply(insertedVnodeQueue, vnode.data.pendingInsert)
vnode.data.pendingInsert = null
}
vnode.elm = vnode.componentInstance.$el
if (isPatchable(vnode)) {
invokeCreateHooks(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
setScope(vnode)
} else {
// empty component root.
// skip all element-related modules except for ref (#3455)
registerRef(vnode)
// make sure to invoke the insert hook
insertedVnodeQueue.push(vnode)
}
}
function reactivateComponent (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm) {
let i
// hack for #4339: a reactivated component with inner transition
// does not trigger because the inner node's created hooks are not called
// again. It's not ideal to involve module-specific logic in here but
// there doesn't seem to be a better way to do it.
let innerNode = vnode
while (innerNode.componentInstance) {
innerNode = innerNode.componentInstance._vnode
if (isDef(i = innerNode.data) && isDef(i = i.transition)) {
for (i = 0; i < cbs.activate.length; ++i) {
cbs.activate[i](emptyNode, innerNode)
}
insertedVnodeQueue.push(innerNode)
break
}
}
// unlike a newly created component,
// a reactivated keep-alive component doesn't insert itself
insert(parentElm, vnode.elm, refElm)
}
function insert (parent, elm, ref) {
if (isDef(parent)) {
if (isDef(ref)) {
if (nodeOps.parentNode(ref) === parent) {
nodeOps.insertBefore(parent, elm, ref)
}
} else {
nodeOps.appendChild(parent, elm)
}
}
}
function createChildren (vnode, children, insertedVnodeQueue) {
if (Array.isArray(children)) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
checkDuplicateKeys(children)
}
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; ++i) {
createElm(children[i], insertedVnodeQueue, vnode.elm, null, true, children, i)
}
} else if (isPrimitive(vnode.text)) {
nodeOps.appendChild(vnode.elm, nodeOps.createTextNode(String(vnode.text)))
}
}
function isPatchable (vnode) {
while (vnode.componentInstance) {
vnode = vnode.componentInstance._vnode
}
return isDef(vnode.tag)
}
function invokeCreateHooks (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) {
for (let i = 0; i < cbs.create.length; ++i) {
cbs.create[i](emptyNode, vnode)
}
i = vnode.data.hook // Reuse variable
if (isDef(i)) {
if (isDef(i.create)) i.create(emptyNode, vnode)
if (isDef(i.insert)) insertedVnodeQueue.push(vnode)
}
}
// set scope id attribute for scoped CSS.
// this is implemented as a special case to avoid the overhead
// of going through the normal attribute patching process.
function setScope (vnode) {
let i
if (isDef(i = vnode.fnScopeId)) {
nodeOps.setStyleScope(vnode.elm, i)
} else {
let ancestor = vnode
while (ancestor) {
if (isDef(i = ancestor.context) && isDef(i = i.$options._scopeId)) {
nodeOps.setStyleScope(vnode.elm, i)
}
ancestor = ancestor.parent
}
}
// for slot content they should also get the scopeId from the host instance.
if (isDef(i = activeInstance) &&
i !== vnode.context &&
i !== vnode.fnContext &&
isDef(i = i.$options._scopeId)
) {
nodeOps.setStyleScope(vnode.elm, i)
}
}
function addVnodes (parentElm, refElm, vnodes, startIdx, endIdx, insertedVnodeQueue) {
for (; startIdx <= endIdx; ++startIdx) {
createElm(vnodes[startIdx], insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, refElm, false, vnodes, startIdx)
}
}
function invokeDestroyHook (vnode) {
let i, j
const data = vnode.data
if (isDef(data)) {
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.destroy)) i(vnode)
for (i = 0; i < cbs.destroy.length; ++i) cbs.destroy[i](vnode)
}
if (isDef(i = vnode.children)) {
for (j = 0; j < vnode.children.length; ++j) {
invokeDestroyHook(vnode.children[j])
}
}
}
function removeVnodes (parentElm, vnodes, startIdx, endIdx) {
for (; startIdx <= endIdx; ++startIdx) {
const ch = vnodes[startIdx]
if (isDef(ch)) {
if (isDef(ch.tag)) {
removeAndInvokeRemoveHook(ch)
invokeDestroyHook(ch)
} else { // Text node
removeNode(ch.elm)
}
}
}
}
function removeAndInvokeRemoveHook (vnode, rm) {
if (isDef(rm) || isDef(vnode.data)) {
let i
const listeners = cbs.remove.length + 1
if (isDef(rm)) {
// we have a recursively passed down rm callback
// increase the listeners count
rm.listeners += listeners
} else {
// directly removing
rm = createRmCb(vnode.elm, listeners)
}
// recursively invoke hooks on child component root node
if (isDef(i = vnode.componentInstance) && isDef(i = i._vnode) && isDef(i.data)) {
removeAndInvokeRemoveHook(i, rm)
}
for (i = 0; i < cbs.remove.length; ++i) {
cbs.remove[i](vnode, rm)
}
if (isDef(i = vnode.data.hook) && isDef(i = i.remove)) {
i(vnode, rm)
} else {
rm()
}
} else {
removeNode(vnode.elm)
}
}
function updateChildren (parentElm, oldCh, newCh, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) {
let oldStartIdx = 0
let newStartIdx = 0
let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1
let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0]
let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx]
let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1
let newStartVnode = newCh[0]
let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx]
let oldKeyToIdx, idxInOld, vnodeToMove, refElm
// removeOnly is a special flag used only by <transition-group>
// to ensure removed elements stay in correct relative positions
// during leaving transitions
const canMove = !removeOnly
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
checkDuplicateKeys(newCh)
}
while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) {
if (isUndef(oldStartVnode)) {
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] // Vnode has been moved left
} else if (isUndef(oldEndVnode)) {
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx)
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) {
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newEndIdx)
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) { // Vnode moved right
patchVnode(oldStartVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newEndIdx)
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, nodeOps.nextSibling(oldEndVnode.elm))
oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx]
newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx]
} else if (sameVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) { // Vnode moved left
patchVnode(oldEndVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx)
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm, oldStartVnode.elm)
oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx]
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
} else {
if (isUndef(oldKeyToIdx)) oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx(oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
idxInOld = isDef(newStartVnode.key)
? oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key]
: findIdxInOld(newStartVnode, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
if (isUndef(idxInOld)) { // New element
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx)
} else {
vnodeToMove = oldCh[idxInOld]
if (sameVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode)) {
patchVnode(vnodeToMove, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, newCh, newStartIdx)
oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined
canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore(parentElm, vnodeToMove.elm, oldStartVnode.elm)
} else {
// same key but different element. treat as new element
createElm(newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm, false, newCh, newStartIdx)
}
}
newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx]
}
}
if (oldStartIdx > oldEndIdx) {
refElm = isUndef(newCh[newEndIdx + 1]) ? null : newCh[newEndIdx + 1].elm
addVnodes(parentElm, refElm, newCh, newStartIdx, newEndIdx, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else if (newStartIdx > newEndIdx) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx)
}
}
function checkDuplicateKeys (children) {
const seenKeys = {}
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
const vnode = children[i]
const key = vnode.key
if (isDef(key)) {
if (seenKeys[key]) {
warn(
`Duplicate keys detected: '${key}'. This may cause an update error.`,
vnode.context
)
} else {
seenKeys[key] = true
}
}
}
}
function findIdxInOld (node, oldCh, start, end) {
for (let i = start; i < end; i++) {
const c = oldCh[i]
if (isDef(c) && sameVnode(node, c)) return i
}
}
function patchVnode (
oldVnode,
vnode,
insertedVnodeQueue,
ownerArray,
index,
removeOnly
) {
if (oldVnode === vnode) {
return
}
if (isDef(vnode.elm) && isDef(ownerArray)) {
// clone reused vnode
vnode = ownerArray[index] = cloneVNode(vnode)
}
const elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm
if (isTrue(oldVnode.isAsyncPlaceholder)) {
if (isDef(vnode.asyncFactory.resolved)) {
hydrate(oldVnode.elm, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else {
vnode.isAsyncPlaceholder = true
}
return
}
// reuse element for static trees.
// note we only do this if the vnode is cloned -
// if the new node is not cloned it means the render functions have been
// reset by the hot-reload-api and we need to do a proper re-render.
if (isTrue(vnode.isStatic) &&
isTrue(oldVnode.isStatic) &&
vnode.key === oldVnode.key &&
(isTrue(vnode.isCloned) || isTrue(vnode.isOnce))
) {
vnode.componentInstance = oldVnode.componentInstance
return
}
let i
const data = vnode.data
if (isDef(data) && isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.prepatch)) {
i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
const oldCh = oldVnode.children
const ch = vnode.children
if (isDef(data) && isPatchable(vnode)) {
for (i = 0; i < cbs.update.length; ++i) cbs.update[i](oldVnode, vnode)
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.update)) i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
if (isUndef(vnode.text)) {
if (isDef(oldCh) && isDef(ch)) {
if (oldCh !== ch) updateChildren(elm, oldCh, ch, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly)
} else if (isDef(ch)) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
checkDuplicateKeys(ch)
}
if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
addVnodes(elm, null, ch, 0, ch.length - 1, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else if (isDef(oldCh)) {
removeVnodes(elm, oldCh, 0, oldCh.length - 1)
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.text)) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, '')
}
} else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text) {
nodeOps.setTextContent(elm, vnode.text)
}
if (isDef(data)) {
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.postpatch)) i(oldVnode, vnode)
}
}
function invokeInsertHook (vnode, queue, initial) {
// delay insert hooks for component root nodes, invoke them after the
// element is really inserted
if (isTrue(initial) && isDef(vnode.parent)) {
vnode.parent.data.pendingInsert = queue
} else {
for (let i = 0; i < queue.length; ++i) {
queue[i].data.hook.insert(queue[i])
}
}
}
let hydrationBailed = false
// list of modules that can skip create hook during hydration because they
// are already rendered on the client or has no need for initialization
// Note: style is excluded because it relies on initial clone for future
// deep updates (#7063).
const isRenderedModule = makeMap('attrs,class,staticClass,staticStyle,key')
// Note: this is a browser-only function so we can assume elms are DOM nodes.
function hydrate (elm, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, inVPre) {
let i
const { tag, data, children } = vnode
inVPre = inVPre || (data && data.pre)
vnode.elm = elm
if (isTrue(vnode.isComment) && isDef(vnode.asyncFactory)) {
vnode.isAsyncPlaceholder = true
return true
}
// assert node match
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (!assertNodeMatch(elm, vnode, inVPre)) {
return false
}
}
if (isDef(data)) {
if (isDef(i = data.hook) && isDef(i = i.init)) i(vnode, true /* hydrating */)
if (isDef(i = vnode.componentInstance)) {
// child component. it should have hydrated its own tree.
initComponent(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
return true
}
}
if (isDef(tag)) {
if (isDef(children)) {
// empty element, allow client to pick up and populate children
if (!elm.hasChildNodes()) {
createChildren(vnode, children, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else {
// v-html and domProps: innerHTML
if (isDef(i = data) && isDef(i = i.domProps) && isDef(i = i.innerHTML)) {
if (i !== elm.innerHTML) {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
typeof console !== 'undefined' &&
!hydrationBailed
) {
hydrationBailed = true
console.warn('Parent: ', elm)
console.warn('server innerHTML: ', i)
console.warn('client innerHTML: ', elm.innerHTML)
}
return false
}
} else {
// iterate and compare children lists
let childrenMatch = true
let childNode = elm.firstChild
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
if (!childNode || !hydrate(childNode, children[i], insertedVnodeQueue, inVPre)) {
childrenMatch = false
break
}
childNode = childNode.nextSibling
}
// if childNode is not null, it means the actual childNodes list is
// longer than the virtual children list.
if (!childrenMatch || childNode) {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
typeof console !== 'undefined' &&
!hydrationBailed
) {
hydrationBailed = true
console.warn('Parent: ', elm)
console.warn('Mismatching childNodes vs. VNodes: ', elm.childNodes, children)
}
return false
}
}
}
}
if (isDef(data)) {
let fullInvoke = false
for (const key in data) {
if (!isRenderedModule(key)) {
fullInvoke = true
invokeCreateHooks(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
break
}
}
if (!fullInvoke && data['class']) {
// ensure collecting deps for deep class bindings for future updates
traverse(data['class'])
}
}
} else if (elm.data !== vnode.text) {
elm.data = vnode.text
}
return true
}
function assertNodeMatch (node, vnode, inVPre) {
if (isDef(vnode.tag)) {
return vnode.tag.indexOf('vue-component') === 0 || (
!isUnknownElement(vnode, inVPre) &&
vnode.tag.toLowerCase() === (node.tagName && node.tagName.toLowerCase())
)
} else {
return node.nodeType === (vnode.isComment ? 8 : 3)
}
}
return function patch (oldVnode, vnode, hydrating, removeOnly) {
if (isUndef(vnode)) {
if (isDef(oldVnode)) invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
return
}
let isInitialPatch = false
const insertedVnodeQueue = []
if (isUndef(oldVnode)) {
// empty mount (likely as component), create new root element
isInitialPatch = true
createElm(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)
} else {
const isRealElement = isDef(oldVnode.nodeType)
if (!isRealElement && sameVnode(oldVnode, vnode)) {
// patch existing root node
patchVnode(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, null, null, removeOnly)
} else {
if (isRealElement) {
// mounting to a real element
// check if this is server-rendered content and if we can perform
// a successful hydration.
if (oldVnode.nodeType === 1 && oldVnode.hasAttribute(SSR_ATTR)) {
oldVnode.removeAttribute(SSR_ATTR)
hydrating = true
}
if (isTrue(hydrating)) {
if (hydrate(oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)) {
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, true)
return oldVnode
} else if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
warn(
'The client-side rendered virtual DOM tree is not matching ' +
'server-rendered content. This is likely caused by incorrect ' +
'HTML markup, for example nesting block-level elements inside ' +
'<p>, or missing <tbody>. Bailing hydration and performing ' +
'full client-side render.'
)
}
}
// either not server-rendered, or hydration failed.
// create an empty node and replace it
oldVnode = emptyNodeAt(oldVnode)
}
// replacing existing element
const oldElm = oldVnode.elm
const parentElm = nodeOps.parentNode(oldElm)
// create new node
createElm(
vnode,
insertedVnodeQueue,
// extremely rare edge case: do not insert if old element is in a
// leaving transition. Only happens when combining transition +
// keep-alive + HOCs. (#4590)
oldElm._leaveCb ? null : parentElm,
nodeOps.nextSibling(oldElm)
)
// update parent placeholder node element, recursively
if (isDef(vnode.parent)) {
let ancestor = vnode.parent
const patchable = isPatchable(vnode)
while (ancestor) {
for (let i = 0; i < cbs.destroy.length; ++i) {
cbs.destroy[i](ancestor)
}
ancestor.elm = vnode.elm
if (patchable) {
for (let i = 0; i < cbs.create.length; ++i) {
cbs.create[i](emptyNode, ancestor)
}
// #6513
// invoke insert hooks that may have been merged by create hooks.
// e.g. for directives that uses the "inserted" hook.
const insert = ancestor.data.hook.insert
if (insert.merged) {
// start at index 1 to avoid re-invoking component mounted hook
for (let i = 1; i < insert.fns.length; i++) {
insert.fns[i]()
}
}
} else {
registerRef(ancestor)
}
ancestor = ancestor.parent
}
}
// destroy old node
if (isDef(parentElm)) {
removeVnodes(parentElm, [oldVnode], 0, 0)
} else if (isDef(oldVnode.tag)) {
invokeDestroyHook(oldVnode)
}
}
}
invokeInsertHook(vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, isInitialPatch)
return vnode.elm
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
415
416
417
418
419
420
421
422
423
424
425
426
427
428
429
430
431
432
433
434
435
436
437
438
439
440
441
442
443
444
445
446
447
448
449
450
451
452
453
454
455
456
457
458
459
460
461
462
463
464
465
466
467
468
469
470
471
472
473
474
475
476
477
478
479
480
481
482
483
484
485
486
487
488
489
490
491
492
493
494
495
496
497
498
499
500
501
502
503
504
505
506
507
508
509
510
511
512
513
514
515
516
517
518
519
520
521
522
523
524
525
526
527
528
529
530
531
532
533
534
535
536
537
538
539
540
541
542
543
544
545
546
547
548
549
550
551
552
553
554
555
556
557
558
559
560
561
562
563
564
565
566
567
568
569
570
571
572
573
574
575
576
577
578
579
580
581
582
583
584
585
586
587
588
589
590
591
592
593
594
595
596
597
598
599
600
601
602
603
604
605
606
607
608
609
610
611
612
613
614
615
616
617
618
619
620
621
622
623
624
625
626
627
628
629
630
631
632
633
634
635
636
637
638
639
640
641
642
643
644
645
646
647
648
649
650
651
652
653
654
655
656
657
658
659
660
661
662
663
664
665
666
667
668
669
670
671
672
673
674
675
676
677
678
679
680
681
682
683
684
685
686
687
688
689
690
691
692
693
694
695
696
697
698
699
700
701
702
703
704
705
706
707
708
709
710
711
712
713
714
715
716
717
718
719
720
721
722
723
724
725
726
727
728
729
730
731
732
733
734
735
736
737
738
739
740
741
createPatchFunction 内部定义了一系列的辅助方法,最终返回了一个 patch 方法,这个方法就赋值给了 vm._update 函数里调用的 vm.patch。patch 是平台相关的,在 Web 和 Weex 环境,它们把虚拟 DOM 映射到 “平台 DOM” 的方法是不同的,并且对 “DOM” 包括的属性模块创建和更新也不尽相同。因此每个平台都有各自的 nodeOps 和 modules,它们的代码需要托管在 src/platforms 这个大目录下。而不同平台的 patch 的主要逻辑部分是相同的,所以这部分公共的部分托管在 core 这个大目录下。
差异化部分只需要通过参数来区别,这里用到了一个函数柯里化的技巧,通过 createPatchFunction 把差异化参数提前固化,这样不用每次调用 patch 的时候都传递 nodeOps 和 modules 了。
回到 patch 方法本身,它接收 4个参数,oldVnode 表示旧的 VNode 节点,它也可以不存在或者是一个 DOM 对象;vnode 表示执行 _render 后返回的 VNode 的节点;hydrating 表示是否是服务端渲染;removeOnly 是给 transition-group 用的。
patch 的逻辑看上去相对复杂,因为它有着非常多的分支逻辑,详细分析查看 虚拟 DOM 与 Diff 算法
createElm 的作用是通过虚拟节点创建真实的 DOM 并插入到它的父节点中。 createComponent 方法目的是尝试创建子组件。
createChildren 的逻辑很简单,实际上是遍历子虚拟节点,递归调用 createElm,这是一种常用的深度优先的遍历算法,这里要注意的一点是在遍历过程中会把 vnode.elm 作为父容器的 DOM 节点占位符传入。
接着再调用 invokeCreateHooks 方法执行所有的 create 的钩子并把 vnode push 到 insertedVnodeQueue 中。
最后调用 insert 方法把 DOM 插入到父节点中,因为是递归调用,子元素会优先调用 insert,所以整个 vnode 树节点的插入顺序是先子后父。
# 小结
- Vue 如何实现数据驱动?
- Vue 如何将模板和数据渲染成最终的 DOM?
- Vue 初始化的过程是怎样的?
- new Vue() 发生了什么?
- 生命周期过程过程是什么?

_init()初始化数据、状态等- 处理组件配置项
- 初始化根组件时进行了选项合并操作,将全局配置合并到根组件的局部配置上
- 初始化每个子组件时做了一些性能优化,将组件配置对象上的一些深层次属性放到
vm.$options选项中,以提高代码的执行效率
- 初始化组件实例的关系属性,比如
$parent、$children、$root、$refs等 - 处理自定义事件
- 调用
beforeCreate钩子函数 - 初始化组件的
inject配置项,得到ret[key] = val形式的配置对象,然后对该配置对象进行浅层的响应式处理(只处理了对象第一层数据),并代理每个 key 到 vm 实例上 - 数据响应式,处理 props、methods、data、computed、watch 等选项
- 解析组件配置项上的 provide 对象,将其挂载到 vm._provided 属性上
- 调用
created钩子函数 - 如果发现配置项上有 el 选项,则自动调用 mount 方法,反之,没提供 el 选项则必须调用
$mount
- 处理组件配置项
compile 编译。
$mount()执行mountComponent, $mount 扩展把 template 和 el 编译render函数- Parse 解析
- Parse 会用正则等方式解析 template 模版中的指令、class、style 等数据,形成 AST。
- Optimize 优化
- Optimize 的主要作用是标记 static 静态节点,这时 Vue 在编译过程中的优化,后面当 update 更新界面时,会有一个 patch 的过程,diff 算法会直接跳过静态节点,从而减少了比较的过程,优化了 patch 的性能。
- Generate 生成
- Generate 是将 AST 转化成 render functio字符串的过程,得到结果是 render 的字符串以及 staticRenderFns 字符串。 在经历过 Parse、Optimize 与 Generate 这三个阶段之后,组件中就会得到用于渲染 VNode 所需的 render 函数了。
- Parse 解析
定义
updateComponent更新函数。mountComponent() 里面定义了updateComponent并 new watcher 实例。new watcher 会走一次 get 方法 触发依赖收集 ,通知 watcher.update。执行
render生成虚拟DOM。updateComponent() 先走 _render 函数把节点转化成 vnode 传给_update()转化为真实 DOM _update(): 最终是把虚拟 dom 转化为真实 dom。经过一系列新旧节点对比,走 patch() 打补丁
打补丁 patch(): createElm() 创建子组件 执行他们的 init 方法(里面是解析->优化->生成)
结合 生命周期过程 进一步理解。
# 问题
# Q1:Vue 的初始化过程都做了什么?
- 处理组件配置项
- 初始化根组件时进行了选项合并操作,将全局配置合并到根组件的局部配置上
- 初始化每个子组件时做了一些性能优化,将组件配置对象上的一些深层次属性放到
vm.$options选项中,以提高代码的执行效率
- 初始化组件实例的关系属性,比如
$parent、$children、$root、$refs等 - 处理自定义事件
- 调用
beforeCreate钩子函数 - 初始化组件的
inject配置项,得到ret[key] = val形式的配置对象,然后对该配置对象进行浅层的响应式处理(只处理了对象第一层数据),并代理每个 key 到 vm 实例上 - 数据响应式,处理 props、methods、data、computed、watch 等选项
- 解析组件配置项上的 provide 对象,将其挂载到 vm._provided 属性上
- 调用
created钩子函数 - 如果发现配置项上有 el 选项,则自动调用 mount 方法,反之,没提供 el 选项则必须调用
$mount - 接下来则进入挂载阶段
# Q2:beforeCreate 钩子函数前完成了什么?
beforeCreate之前,主要是在处理vm实例上的各种属性配置和自定义事件属性。首先合并了组件的配置项挂载到全局vm.$options上。初始化组件实例关系属性:$parent、$children、$root、$refs等等;初始化自定义事件监听;最后初始化组件插槽,作用域插槽,render函数等(createElement),同时定义了组件$attr、$listeners属性。
所以,在 beforeCreate 钩子内不能通过 this 访问 prop、data 等。因为在 vue 初始化阶段,beforeCreate 阶段 data 中的变量还没有被挂载到 this 上,这个时候访问值会是 undefined。beforeCreate 这个钩子在平时业务开发中用的比较少,而像插件内部的 install 方法通过 Vue.use 方法安装时一般会选在 beforeCreate 这个钩子内执行,vue-router 和 vuex 就是这么干的。
# Q3:created 钩子函数前完成了什么?
首先初始化好 inject 配置项,再初始化各种响应式数据和方法如:props、methods、data、computed、watch,最后初始化 provided 配置项(vm.provided)。
# Q4:初始化函数 initInjections(vm)、 initState(vm) 、initProvide(vm) 顺序是否可变化?
inject 配置项是注入数据,在后续的 computed、data 中有可能会用到 inject 的数据,proive 配置项是解析数据,需要等待响应式数据和方法初始化完成后执行,所以顺序不能变。
# Q5:methods 内的方法可以使用箭头函数么吗?
不可以使用箭头函数的,因为箭头函数的this是定义时就绑定的。在vue的内部,methods内每个方法的上下文是当前的vm组件实例,methods[key].bind(vm),而如果使用使用箭头函数,函数的上下文就变成了父级的上下文,也就是undefined了,结果就是通过undefined访问任何变量都会报错。
# Q6: 父子组件钩子的执行顺序?
首先会执行父组件的初始化过程,所以会依次执行beforeCreate、created、在执行挂载前又会执行beforeMount钩子,不过在生成真实dom的__patch__过程中遇到嵌套子组件后又会转为去执行子组件的初始化钩子beforeCreate、created,子组件在挂载前会执行beforeMounte,再完成子组件的Dom创建后执行mounted。这个父组件的__patch__过程才算完成,最后执行父组件的mounted钩子,这就是它们的执行顺序。执行顺序如下:
parent beforeCreate
parent created
parent beforeMounte
child beforeCreate
child created
child beforeMounte
child mounted
parent mounted
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# Q7. Vue 的 mixin 及合并策略 ?
mixin(混入),提供了一种非常灵活的方式,来分发 Vue 组件中的可复用功能。本质其实就是一个js对象,它可以包含我们组件中任意功能选项,如data、components、methods、created、computed等等。我们只要将共用的功能以对象的方式传入 mixins选项中,当组件使用 mixins对象时所有mixins对象的选项都将被混入该组件本身的选项中来。在Vue中可以局部混入或全局混入。全局混入常用于插件的编写。
注意
当组件存在与mixin对象相同的选项的时候,进行递归合并的时候组件的选项会覆盖mixin的选项。是如果相同选项为生命周期钩子的时候,会合并成一个数组(队列),先执行mixin的钩子,再执行组件的钩子。
关于Vue的几种类型的合并策略
替换型
- 替换型合并有
inject、props、methods、computed。同名的会被后者替代。
- 替换型合并有
合并型
合并型有:
datamergeData函数遍历了要合并的 data 的所有属性,然后根据不同情况进行合并:- 当目标 data 对象不包含当前属性时,调用
set方法进行合并(set方法其实就是一些合并重新赋值的方法) - 当目标 data 对象包含当前属性并且当前值为纯对象时,递归合并当前对象值,这样做是为了防止对象存在新增属性。
- 当目标 data 对象不包含当前属性时,调用
队列型
- 队列型合并有:全部生命周期钩子和
watch。生命周期钩子和watch被合并为一个数组,然后正序遍历一次执行。
- 队列型合并有:全部生命周期钩子和
叠加型
- 叠加型合并有:
component、directives、filters。叠加型主要是通过原型链进行层层的叠加。
- 叠加型合并有:
