# Pinia 原理
# Vuex5 提案
Vuex5 提案 (opens new window),旨在解决 Vuex4 的痛点:
- 支持 store creation、 Options API 和 Composition API 的语法。
- 没有 Mutation,仅有 State、Getter 和 Actions, Actions 中可直接改变 state。
- 没有 Nested Modules 嵌套模块(去掉 namespace 功能),只有 Store。
- 支持完整的 TypeScript 支持与类型推导。
- 支持自动代码分割。
Vuex5 引入了关于如何定义、创建和管理 Store 的全新想法。这和 Pinia 非常接近:
- store:可理解为一个单独的组件,其行为与 Vuex3 和 4 中的 Modules 非常相似。新的 Vuex 实例将充当这些 Store 的容器。pinia 采用模块式管理,每个 store 都是独立的,互相不影响。
- state:与 Vuex3 和 4 中的 state 相同。但是在 Vuex5 中,它必须是一个函数。
- getters:类似于 Vuex3 和 4 中的 getters,但它不会接收任何参数。要引用 state 需通过
this上下文访问。 - actions: 类似于 Vuex 3 和 4 中的 action,但它可以直接改变 state。它也可能是 async 函数。要引用 state 或 getter 需通过
this上下文访问。
# Pinia 的使用
# 定义 Store
- 在
src/main.js中导入createPinia方法,通过createPinia方法创建 Pinia 的实例后,再通过app.use方法注册 Pinia:
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import App from './App.vue'
const pinia = createPinia()
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(pinia).mount('#app')
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
- 通过 Pinia 的
defineStore方法定义了一个 store,store 内部通过 state 返回一个对象,并且通过 Actions 修改 state。这里使用的语法和 Vuex 比较类似,只是删除了 Mutation 的概念,统一使用 Actions:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
// Options API 风格
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {
state: () => ({ count: 0, name: 'Eduardo' }), // 必须是函数,推荐使用箭头函数
getters: {
doubleCount: (state) => state.count * 2,
},
actions: {
increment() {
this.count++
},
},
})
// Composition API 风格,用使用 ref 或者 reactive 包裹 state
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', () => {
const count = ref(0)
const doubleCount = computed(() => count.value * 2)
function increment() {
count.value++
}
return { count, doubleCount, increment }
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
在 Option Store 中,可以理解 Store 为一个组件:
- state 是 store 的数据 (data)
- getters 是 store 的计算属性 (computed)
- actions 是 store 的方法 (methods)。
在 Setup Store 中,
- ref() 就是 state 属性
- computed() 就是 getters
- function() 就是 actions、
注意,要让 pinia 正确识别 state,你必须在 setup store 中返回 state 的所有属性。这意味着,不能在 store 中使用私有属性。不完整的返回会影响 SSR ,开发工具和其他插件的正常运行。
为了从 store 中提取属性时保持其响应性,需要使用 storeToRefs()。它将为每一个响应式属性创建引用。当你只使用 store 的状态而不调用任何 action 时,它会非常有用。请注意,你可以直接从 store 中解构 action,因为它们也被绑定到 store 上:
<script setup>
import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'
const store = useCounterStore()
// `name` 和 `doubleCount` 是响应式的 ref
// 同时通过插件添加的属性也会被提取为 ref
// 并且会跳过所有的 action 或非响应式 (不是 ref 或 reactive) 的属性
const { name, doubleCount } = storeToRefs(store)
// 作为 action 的 increment 可以直接解构
const { increment } = store
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
此外,Setup store 也可以依赖于全局提供的属性,比如路由。任何应用层面提供的属性都可以在 store 中使用 inject() 访问,就像在组件中一样:
import { inject } from 'vue'
import { useRoute } from 'vue-router'
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useSearchFilters = defineStore('search-filters', () => {
const route = useRoute()
// 这里假定 `app.provide('appProvided', 'value')` 已经调用过
const appProvided = inject('appProvided')
// ...
return {
// ... 不用返回 route 它不属于 store。
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 使用 State
# 访问 state
默认情况下,你可以通过 store 实例访问 state,直接对其进行读写。
const store = useStore()
store.count++
2
3
# 重置 state
使用 Option API 时,你可以通过调用 store 的 $reset() 方法将 state 重置为初始值。
const store = useStore()
store.$reset()
2
3
在 $reset() 内部,会调用 state() 函数来创建一个新的状态对象,并用它替换当前状态。
在 Setup Stores 中,您需要创建自己的 $reset() 方法:
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', () => {
const count = ref(0)
function $reset() {
count.value = 0
}
return { count, $reset }
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 变更 state
除了用 store.count++ 直接改变 store,你还可以调用 $patch 方法。它允许你用一个 state 的补丁对象在同一时间更改多个属性:
store.$patch({
count: store.count + 1,
age: 120,
name: 'DIO',
})
2
3
4
5
$patch 方法也接受一个函数来组合这种难以用补丁对象实现的变更:
store.$patch((state) => {
state.items.push({ name: 'shoes', quantity: 1 })
state.hasChanged = true
})
2
3
4
注意
两种变更 store 方法的主要区别是,$patch() 允许你将多个变更归入 devtools 的同一个条目中。同时请注意,直接修改 state,$patch() 也会出现在 devtools 中,而且可以进行 time travel (在 Vue 3 中还没有)。
# 替换 state
你不能完全替换掉 store 的 state,因为那样会破坏其响应性。但是,你可以 patch 它:
// 这实际上并没有替换`$state`
store.$state = { count: 24 }
// 在它内部调用 `$patch()`:
store.$patch({ count: 24 })
// 你也可以通过变更 pinia 实例的 state 来设置整个应用的初始 state。这常用于 SSR 中的激活过程:
pinia.state.value = {}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 订阅 state
通过 store 的 $subscribe() 方法侦听 state 及其变化。比起普通的 watch(),使用 $subscribe() 的好处是 subscriptions 在 patch 后只触发一次:
cartStore.$subscribe((mutation, state) => {
// import { MutationType } from 'pinia'
mutation.type // 'direct' | 'patch object' | 'patch function'
// 和 cartStore.$id 一样
mutation.storeId // 'cart'
// 只有 mutation.type === 'patch object'的情况下才可用
mutation.payload // 传递给 cartStore.$patch() 的补丁对象。
// 每当状态发生变化时,将整个 state 持久化到本地存储。
localStorage.setItem('cart', JSON.stringify(state))
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
默认情况下,state subscription 会被绑定到添加它们的组件上 (如果 store 在组件的 setup() 里面)。这意味着,当该组件被卸载时,它们将被自动删除。如果你想在组件卸载后依旧保留它们,请将 { detached: true } 作为第二个参数,以将 state subscription 从当前组件中分离:
<script setup>
const someStore = useSomeStore()
// 此订阅器即便在组件卸载之后仍会被保留
someStore.$subscribe(callback, { detached: true })
</script>
2
3
4
5
你可以在 pinia 实例上使用 watch() 函数侦听整个 state。
watch(
pinia.state,
(state) => {
// 每当状态发生变化时,将整个 state 持久化到本地存储。
localStorage.setItem('piniaState', JSON.stringify(state))
},
{ deep: true }
)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Getter、Action、Plugin 的使用见官网 (opens new window)
# Pinia 的实现
# 创建 Pinia 实例
通过 effectScope 创建一个作用域对象,并且通过 ref 创建了响应式的数据对象 state。然后通过 install 方法支持了通过 app.use 的注册,内部通过 provide 的语法和全局的 $pinia 变量配置 Pinia 对象,并且通过 use 方法和 toBeInstalled 数组实现了 Pinia 的插件机制。最后还通过 pinia.use(devtoolsPlugin) 实现了对 VueDevtools 的支持。
effectScope:这是一个 Vue 3.x 高阶的响应式的 api,能够对这个 effect 里面的响应式副作用(计算属性、监听器)统一进行操作处理,例如调用 stop 停止监听拦截等。
// packages/pinia/src/createPinia.ts
export function createPinia(): Pinia {
const scope = effectScope(true)
// NOTE: here we could check the window object for a state and directly set it
// if there is anything like it with Vue 3 SSR
const state = scope.run<Ref<Record<string, StateTree>>>(() =>
ref<Record<string, StateTree>>({})
)!
let _p: Pinia['_p'] = [] // 所有需要安装的插件
// plugins added before calling app.use(pinia)
let toBeInstalled: PiniaPlugin[] = []
// markRaw:标记该 pinia 不会被响应式转换和监听,能够节约内存的使用,提高运行效率
const pinia: Pinia = markRaw({
install(app: App) { // vue.use(pinia) 执行逻辑
// this allows calling useStore() outside of a component setup after
// installing pinia's plugin
setActivePinia(pinia)
if (!isVue2) {
pinia._a = app // app实例
app.provide(piniaSymbol, pinia) // 通过 provide 来注入 pinia 实例
app.config.globalProperties.$pinia = pinia // 在 vue 项目当中设置全局属性 $pinia
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (__USE_DEVTOOLS__ && IS_CLIENT) {
registerPiniaDevtools(app, pinia)
}
toBeInstalled.forEach((plugin) => _p.push(plugin)) // 处理未执行插件
toBeInstalled = []
}
},
// pinia 使用插件时候调用执行,将 pinia 插件都先塞到一个 _p 的数组当中,后续再进行初始化执行
use(plugin) {
if (!this._a && !isVue2) {
toBeInstalled.push(plugin)
} else {
_p.push(plugin)
}
return this
},
_p,
// it's actually undefined here
// @ts-expect-error
_a: null,
_e: scope, // pinia 的 effect 作用域对象,每个store都是单独的scope
_s: new Map<string, StoreGeneric>(), // 以 Map 的数据结构形式存储 pinia 数据仓库 store,类似 state
state, // pinia所有 state 的合集, key 为 pinia 的 id, value为 store下的所有 state(所有可访问变量)
})
// pinia devtools rely on dev only features so they cannot be forced unless
// the dev build of Vue is used. Avoid old browsers like IE11.
if (__USE_DEVTOOLS__ && typeof Proxy !== 'undefined') {
pinia.use(devtoolsPlugin)
}
return pinia
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
Pinia 实例就是 ref({})包裹的响应式对象,项目中用到的 state 都会挂载到 Pinia 这个响应式对象内部。
# 创建 Store
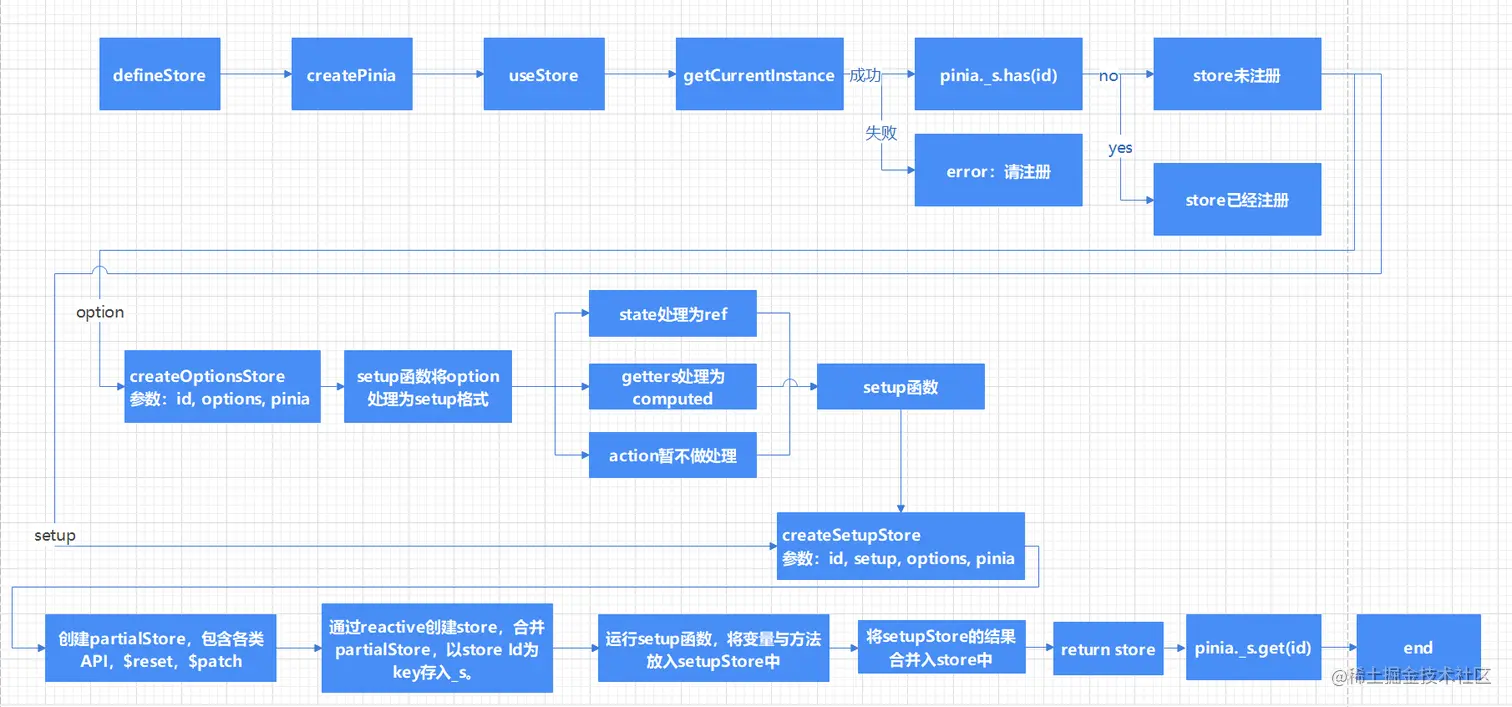
defineStore 利用 TypeScript 函数重载来实现传递不同参数进行数据仓库的初始化处理。其内部通过 useStore 方法去定义 store,并且每个 store 都会标记唯一的 ID。defineStore 里面含有一个 useStore 方法,并且作为其返回值。因此 useStore 才是 Pinia store 的核心创建逻辑。
- 首先通过
getCurrentInstance获取当前组件的实例,如果 useStore 参数没有 Pinia 的话,就使用 inject 去获取 Pinia 实例,这里 inject 的数据就是 createPinia 函数中 install 方法提供的。 - 然后设置
activePinia,项目中可能会存在很多 Pinia 的实例,设置 activePinia 就是设置当前活跃的 Pinia 实例。这个函数的实现方式和 Vue 中的componentInstance很像,每次创建组件的时候都设置当前的组件实例,这样就可以在组件的内部通过getCurrentInstance获取。 - 接着通过
createSetupStore或者createOptionsStore创建组件,这就是两种语法创建 store 的不同执行逻辑。 - 最后通过
pinia._s缓存创建后的 store,_s就是在 createPinia 的时候创建的一个 Map 对象,防止 store 多次重复创建。
// packages\pinia\src\store.ts
export function defineStore(
// TODO: add proper types from above
idOrOptions: any,
setup?: any,
setupOptions?: any
): StoreDefinition {
let id: string
let options:
| DefineStoreOptions<
string,
StateTree,
_GettersTree<StateTree>,
_ActionsTree
>
| DefineSetupStoreOptions<
string,
StateTree,
_GettersTree<StateTree>,
_ActionsTree
>
// 不同参数形式的兼容处理
const isSetupStore = typeof setup === 'function'
if (typeof idOrOptions === 'string') {
id = idOrOptions
// the option store setup will contain the actual options in this case
options = isSetupStore ? setupOptions : setup
} else {
options = idOrOptions
id = idOrOptions.id
if (__DEV__ && typeof id !== 'string') {
throw new Error(
`[🍍]: "defineStore()" must be passed a store id as its first argument.`
)
}
}
// 声明 useStore 函数并且作为 defineStore 函数的返回值
function useStore(pinia?: Pinia | null, hot?: StoreGeneric): StoreGeneric {
// 获取当前 Vue 的组件实例
const hasContext = hasInjectionContext()
pinia =
// in test mode, ignore the argument provided as we can always retrieve a
// pinia instance with getActivePinia()
(__TEST__ && activePinia && activePinia._testing ? null : pinia) ||
(hasContext ? inject(piniaSymbol, null) : null)
// 设置当前 pinia 为当前活跃的 pinia 实例
if (pinia) setActivePinia(pinia)
if (__DEV__ && !activePinia) {
throw new Error(
`[🍍]: "getActivePinia()" was called but there was no active Pinia. Are you trying to use a store before calling "app.use(pinia)"?\n` +
`See https://pinia.vuejs.org/core-concepts/outside-component-usage.html for help.\n` +
`This will fail in production.`
)
}
// 获取当前活跃的 pinia 实例
pinia = activePinia!
// 单例模式:如果 pinia 中已经有对应 id 模块的 store 实例则直接获取该 store 实例返回,否则执行创建 store 逻辑
if (!pinia._s.has(id)) {
// creating the store registers it in `pinia._s`
if (isSetupStore) {
createSetupStore(id, setup, options, pinia)
} else {
createOptionsStore(id, options as any, pinia)
}
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (__DEV__) {
// @ts-expect-error: not the right inferred type
useStore._pinia = pinia
}
}
// 获取对应的 store,_s 属性是 Map 的数据结构对 Pinia 所有模块 store 的存储
const store: StoreGeneric = pinia._s.get(id)!
if (__DEV__ && hot) {
const hotId = '__hot:' + id
const newStore = isSetupStore
? createSetupStore(hotId, setup, options, pinia, true)
: createOptionsStore(hotId, assign({}, options) as any, pinia, true)
hot._hotUpdate(newStore)
// cleanup the state properties and the store from the cache
delete pinia.state.value[hotId]
pinia._s.delete(hotId)
}
if (__DEV__ && IS_CLIENT) {
const currentInstance = getCurrentInstance()
// save stores in instances to access them devtools
if (
currentInstance &&
currentInstance.proxy &&
// avoid adding stores that are just built for hot module replacement
!hot
) {
const vm = currentInstance.proxy
const cache = '_pStores' in vm ? vm._pStores! : (vm._pStores = {})
cache[id] = store
}
}
// StoreGeneric cannot be casted towards Store
return store as any
}
useStore.$id = id
// 返回 store
// 在该 store 被使用之前返回函数不会执行,所以 defineStore 早于在 Vue 种注册 pinia 也不会出现错误。
return useStore
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
# 状态更新
# createOptionsStore
createOptionsStore 内部也是调用了 createSetupStore 来创建 store 对象。通过 assign 方法实现了 setup 函数,这里可以看到 computed 的实现,内部就是通过 pinia._s 缓存获取 store 对象,调用 store 的 getters 方法来模拟,最后依然通过 createSetupStore 创建。
function createOptionsStore<
Id extends string,
S extends StateTree,
G extends _GettersTree<S>,
A extends _ActionsTree,
>(
id: Id,
options: DefineStoreOptions<Id, S, G, A>,
pinia: Pinia,
hot?: boolean
): Store<Id, S, G, A> {
const { state, actions, getters } = options
const initialState: StateTree | undefined = pinia.state.value[id]
let store: Store<Id, S, G, A>
// 如果没有初始化过当前 ID 的 state 则使用 options 的 state 方法创建一个响应式的数据
function setup() {
if (!initialState && (!__DEV__ || !hot)) {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (isVue2) {
set(pinia.state.value, id, state ? state() : {})
} else {
pinia.state.value[id] = state ? state() : {}
}
}
// avoid creating a state in pinia.state.value
// 通过 toRefs 获取一个解构仍能保持响应式的当前 ID 的 state 数据仓库
// 经过 toRefs 处理后,localState.xx.value 就等同于给 state 中的 xx 赋值
const localState =
__DEV__ && hot
? // use ref() to unwrap refs inside state TODO: check if this is still necessary
toRefs(ref(state ? state() : {}).value)
: toRefs(pinia.state.value[id])
return assign(
localState,
actions,
Object.keys(getters || {}).reduce(
(computedGetters, name) => {
if (__DEV__ && name in localState) {
console.warn(
`[🍍]: A getter cannot have the same name as another state property. Rename one of them. Found with "${name}" in store "${id}".`
)
}
// 使用 markRaw 标记对象,防止对象被 Proxy 劫持成为响应式数据
computedGetters[name] = markRaw(
// 使用计算属性处理 options 的 getters -- 也是因为这步操作使得 pinia 的 getters 拥有 Vue.js 的 computed 的能力
computed(() => {
setActivePinia(pinia)
// it was created just before
const store = pinia._s.get(id)!
// allow cross using stores
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (isVue2 && !store._r) return
// @ts-expect-error
// return getters![name].call(context, context)
// TODO: avoid reading the getter while assigning with a global variable
// 将 store 的 this 指向 getters 中实现 getters 中 this 才正常使用
return getters![name].call(store, store)
})
)
return computedGetters
},
{} as Record<string, ComputedRef>
)
)
}
// 最终还是通过 createSetupStore 创建 store
store = createSetupStore(id, setup, options, pinia, hot, true)
return store as any
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
createOptionStore 方法内部最主要还是根据 options 对象里面的数据,在方法内部构建并且封装为 setup 函数,setup 函数当中主要是将 options 参数中的 state 与 getters 属性分别使用 toRefs 和 computed 封装转化为 ref 响应式数据与 computed 计算属性。因为这步操作使得 pinia store 的 state 的里面的属性具有响应式能力及 getters 具有计算属性的能力,actions 属性保持原样作为 setup 函数返回的对象属性,后续会在 createSetupStore 内进行进一步处理。
# createSetupStore - $patch 更新
createSetupStore 函数的实现。这个函数也是 Pinia 中最复杂的函数实现,实现了 $patch、$reset、$dispose、$subscribe、$onAction,其中内部的 $patch 函数可以实现数据的更新。如果传递的参数 partialStateOrMutator 是函数,则直接执行,否则就通过 mergeReactiveObjects 方法合并到 state 中,最后生成 subscriptionMutation 对象,通过 triggerSubscriptions 方法触发数据的更新。
createSetupStore 等方法内部也会通过 Map 的方式实现缓存,并且 setActivePinia 方法可以在多个 Pinia 实例的时候获取当前的实例。
// $patch 函数实现数据的更新
function $patch(
partialStateOrMutator:
| _DeepPartial<UnwrapRef<S>>
| ((state: UnwrapRef<S>) => void)
): void {
let subscriptionMutation: SubscriptionCallbackMutation<S>
isListening = isSyncListening = false
// reset the debugger events since patches are sync
/* istanbul ignore else */
if (__DEV__) {
debuggerEvents = []
}
if (typeof partialStateOrMutator === 'function') {
partialStateOrMutator(pinia.state.value[$id] as UnwrapRef<S>)
subscriptionMutation = {
type: MutationType.patchFunction,
storeId: $id,
events: debuggerEvents as DebuggerEvent[],
}
} else {
mergeReactiveObjects(pinia.state.value[$id], partialStateOrMutator)
subscriptionMutation = {
type: MutationType.patchObject,
payload: partialStateOrMutator,
storeId: $id,
events: debuggerEvents as DebuggerEvent[],
}
}
const myListenerId = (activeListener = Symbol())
nextTick().then(() => {
if (activeListener === myListenerId) {
isListening = true
}
})
isSyncListening = true
// because we paused the watcher, we need to manually call the subscriptions
triggerSubscriptions(
subscriptions,
subscriptionMutation,
pinia.state.value[$id] as UnwrapRef<S>
)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
# $reset 状态重置实现
Options Store 支持重置 state,内部还是通过 $patch 实现状态的重置:
const $reset = isOptionsStore
? function $reset(this: _StoreWithState<Id, S, G, A>) {
const { state } = options as DefineStoreOptions<Id, S, G, A>
const newState: _DeepPartial<UnwrapRef<S>> = state ? state() : {}
// we use a patch to group all changes into one single subscription
this.$patch(($state) => {
// @ts-expect-error: FIXME: shouldn't error?
assign($state, newState)
})
}
: /* istanbul ignore next */
__DEV__
? () => {
throw new Error(
`🍍: Store "${$id}" is built using the setup syntax and does not implement $reset().`
)
}
: noop
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# Store 挂载
通过定义 partialStore 对象去存储 ID、$patch、Pinia 实例,并且新增了 subscribe 方法。再调用 reactive 函数把 partialStore 包裹成响应式对象,通过 pinia._s.set 的方法实现 store 的挂载。
最后我们通过 pinia._s.get 获取的就是 partialStore 对象,defineStore 返回的方法 useStore 就可以通过 useStore 去获取缓存的 Pinia 对象,实现对数据的更新和读取。
这里我们也可以看到,除了直接执行 Action 方法,还可以通过调用内部的 count.$patch({count:count+1}) 的方式来实现数字的累加。
const partialStore = {
_p: pinia,
// _s: scope,
$id,
$onAction: addSubscription.bind(null, actionSubscriptions),
$patch,
$reset,
$subscribe(callback, options = {}) {
const removeSubscription = addSubscription(
subscriptions,
callback,
options.detached,
() => stopWatcher()
)
const stopWatcher = scope.run(() =>
watch(
() => pinia.state.value[$id] as UnwrapRef<S>,
(state) => {
if (options.flush === 'sync' ? isSyncListening : isListening) {
callback(
{
storeId: $id,
type: MutationType.direct,
events: debuggerEvents as DebuggerEvent,
},
state
)
}
},
assign({}, $subscribeOptions, options)
)
)!
return removeSubscription
}
const store: Store<Id, S, G, A> = reactive(
assign({}, partialStore )
)
// store the partial store now so the setup of stores can instantiate each other before they are finished without
// creating infinite loops.
pinia._s.set($id, store)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
# storeToRefs 保证响应式
export function storeToRefs<SS extends StoreGeneric>(
store: SS
): StoreToRefs<SS> {
// See https://github.com/vuejs/pinia/issues/852
// It's easier to just use toRefs() even if it includes more stuff
if (isVue2) {
// @ts-expect-error: toRefs include methods and others
return toRefs(store)
} else {
store = toRaw(store)
const refs = {} as StoreToRefs<SS>
for (const key in store) {
const value = store[key]
if (isRef(value) || isReactive(value)) {
// @ts-expect-error: the key is state or getter
refs[key] =
// ---
toRef(store, key)
}
}
return refs
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
总结:
# Pinia 的优点
- 简化 API
- 统一状态修改:Pinia 将状态修改逻辑统一到 actions 中,不再用 mutations,减少了 mutations 和 actions 的心智负担,使得 API 更加简单直观。
- 减少样板代码:不需要在 actions 中调用 commit 方法来触发 mutations,代码更加简洁。
- 更好的 TypeScript 支持
- 类型推断:Pinia 提供了强大的类型推断能力,减少了手动编写类型的负担。
- 类型安全:通过 TypeScript,可以确保状态管理代码的类型安全,减少运行时错误。
- 灵活性
- 同步和异步:actions 既可以是同步的,也可以是异步的,提供了更大的灵活性。
- 模块化
- 可以将状态管理逻辑拆分成多个 store,每个 store 管理一部分状态,使得代码更加模块化和可维护。
- Composition API 支持,与 Vue 3 集成:Pinia 充分利用了 Vue 3 的 Composition API,使得状态管理逻辑可以与组件模板分离,提高了代码的复用性和组织性。
- 依赖注入
- 全局注册:通过 provide 和 inject 机制,可以轻松地在任何组件中获取 store 实例,无需手动传递 props。
- 模块热替换 (HMR)
- 支持 HMR,使得在开发过程中可以即时看到 store 文件的变化,无需重新加载整个页面。
- 体积更小
- 比 Vuex 体积更小,构建压缩后只有 1KB 左右的大小。
# 问题
# Q1. pinia 或者 vuex5 中 为什么 state 必须是一个函数?
在 Option Store 中,state 必须是一个函数以确保每个实例都有自己的状态副本,避免状态共享问题,确保每个组件或模块的状态独立,从而避免意外的状态污染。这其实与 Vue 实例中的 data 遵循同样的规则一个道理。
当你定义 state 为一个函数时,每次创建一个新的 store 实例时,都会返回一个新的状态对象,从而确保每个组件实例都有自己的独立状态。这样,多个组件或模块使用相同的 store 时,不会互相影响,保证了数据的隔离性和一致性。此外,这种方式使得状态在热重载时也能保持一致性,提升了开发体验。
# Q2. pinia 中状态是为什么能共享,怎么实现的?
在 Vue 3 中,Composition API 通过 setup 函数来定义组件的逻辑。在 setup 函数中,你可以使用 ref 和 reactive 来创建响应式状态。这些状态是局部的,每个组件实例都有自己独立的副本。
Pinia 的状态管理是全局的,所有组件实例共享同一个状态。这是通过以下机制实现的:
- 全局注册和依赖注入:
- Pinia 使用 Vue 3 的 provide 和 inject 机制来全局注册 store,子组件都可以通过 inject 获取这些 store。
- 在根组件中安装 Pinia 后,所有子组件都可以通过 useStore 钩子来获取 store 实例,相同 id 的 store 被不同组件引用,引用的是同一个 store 实例。
- 响应式状态:
- Pinia 使用 reactive 来创建响应式状态对象。
- 当组件通过 useStore 获取 store 实例时,实际上获取的是同一个响应式对象的引用。
# Q3. 为什么访问 defineStore 创建的 state 不需要 .value
state 的数据都会被处理为 ref,访问 ref 是需要 .value,但 pinia 从来没有 .value。原因就是 reactive 中嵌套 ref 的时候,修改 reactive 内的值不需要 .value。将一个 ref 赋值给一个 reactive 属性时,该 ref 会被自动解包:
const count = ref(1)
const obj = reactive({})
obj.count = count
console.log(obj.count) // 1
console.log(obj.count === count.value) // true
2
3
4
5
6
7
